Posted At: Feb 15, 2026 - 62 Views

Imagine charging your phone at an airport, railway station, hotel lobby, or mall. You plug your device into a public USB charging port, and within seconds, your phone begins charging.
But what if that charging port isn’t just supplying power?
What if it’s secretly stealing your data?
This is called a Juice Jacking attack — a growing cybersecurity threat that targets smartphones, tablets, and USB-powered devices.
In this complete guide, you will learn:
- What juice jacking is
- How attackers perform it
- Real-world scenarios
- Different types of juice jacking
- How hackers install malware
- How to prevent it completely
- What students, professionals, and institutes should do
Let’s break it down.
What Is Juice Jacking?
Juice jacking is a type of cyberattack where a hacker uses a compromised USB charging port or cable to steal data or install malware on your device.
The term comes from:
- “Juice” = electrical power
- “Jacking” = hijacking
So basically, attackers hijack your device while it’s charging.
Unlike normal hacking methods that require Wi-Fi or phishing emails, juice jacking happens through physical USB connections.
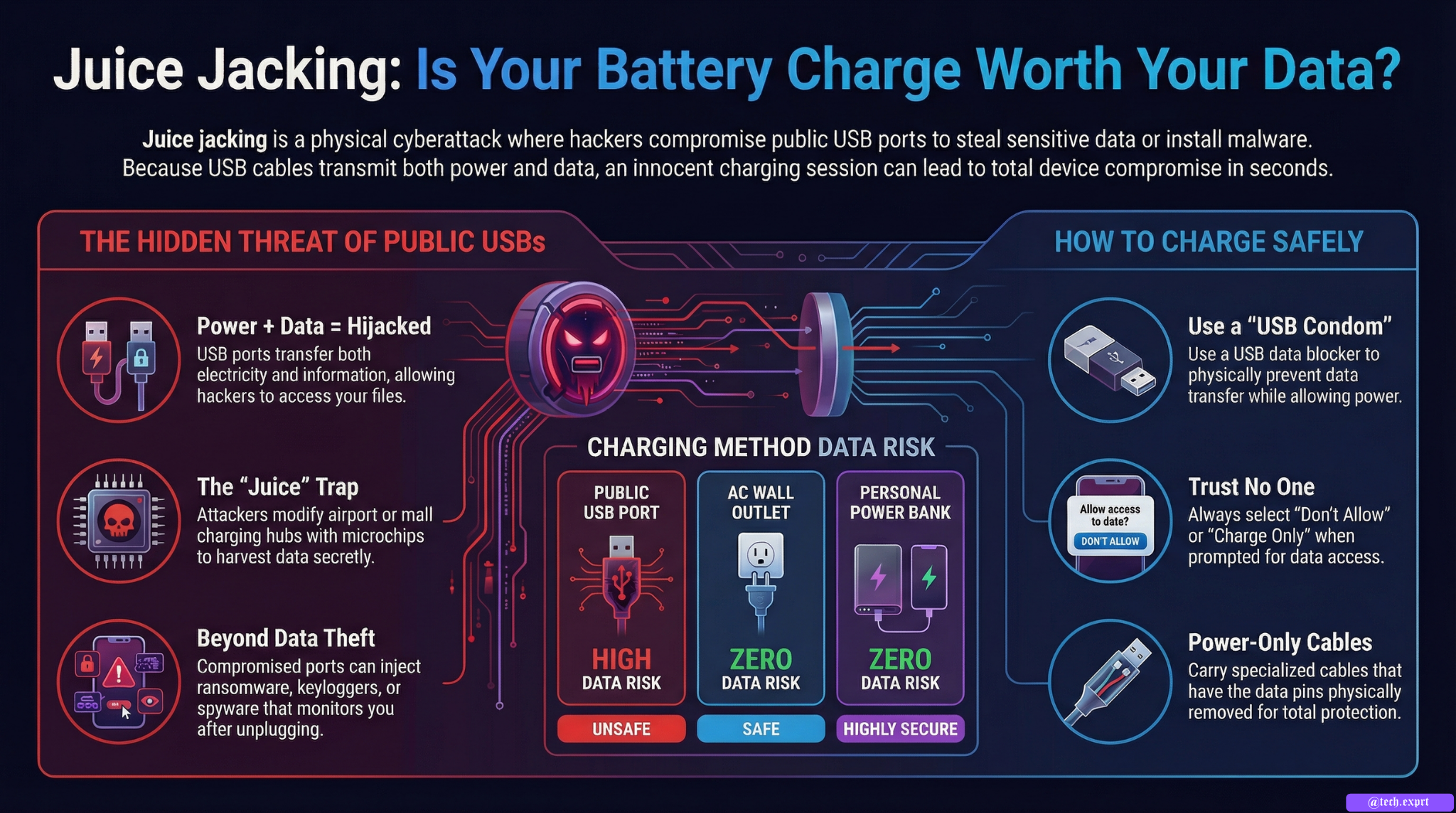
Why Juice Jacking Is Dangerous
Many people believe charging is safe because:
• They are not using Wi-Fi
• They are not downloading anything
• They are not opening suspicious apps
But USB ports can transfer BOTH:
✔ Power
✔ Data
This is the key problem.
If the USB port is compromised, attackers can:
• Copy photos, contacts, files
• Install spyware
• Inject malware
• Lock your device (ransomware)
• Steal login credentials
• Monitor your activities
And all this can happen in seconds.
How Juice Jacking Works (Step-by-Step)
Let’s understand technically how attackers perform this.
Step 1: Compromising a Public Charging Station
Attackers modify:
• Airport USB charging ports
• Mall charging stations
• Hotel lobby charging hubs
• Public kiosks
• Shared charging cables
They either:
• Install a small malicious microcontroller
• Replace internal USB wiring
• Embed a data-harvesting chip
Now the charging station looks normal.
Step 2: Victim Connects Device
When a user plugs their device into:
• USB-A port
• USB-C port
• Micro-USB port
The connection establishes both:
• Power transfer
• Data communication protocol
Most users don’t realize USB is not power-only.
Step 3: Device Trust Prompt (Sometimes Ignored)
On many smartphones, a message appears:
“Trust this device?”
“Allow data access?”
Many users tap “Allow” without thinking.
This grants permission.
Step 4: Data Extraction or Malware Injection
Once permission is granted, the malicious station can:
• Access internal storage
• Copy files
• Install malicious apps
• Create backdoor access
• Inject keyloggers
In some advanced attacks, no permission popup appears due to system vulnerabilities.
Types of Juice Jacking Attacks
There are two main types:
1. Data Theft Juice Jacking
This attack copies sensitive information:
• Contacts
• Photos
• Messages
• Emails
• Business documents
• Banking apps data
Especially dangerous for:
• Business professionals
• Government employees
• Students with exam data
• Digital creators
2. Malware Injection Juice Jacking
This installs malicious software such as:
• Spyware
• Banking trojans
• Keyloggers
• Ransomware
• Remote access tools
This type is more dangerous because:
The attacker can monitor you long after you unplug.
Real-Life Scenarios Where Juice Jacking Happens
Juice jacking commonly occurs in:
• Airports
• Railway stations
• Bus terminals
• Malls
• Conferences
• Hotels
• Tech events
• Educational seminars
People are:
• Low on battery
• In a hurry
• Less cautious
Perfect opportunity for attackers.
Why Public USB Ports Are Risky
Public charging stations:
• Are unattended
• Are used by thousands daily
• Rarely inspected
• Can be easily modified
Unlike power sockets (AC outlets), USB ports directly interact with your device’s data system.
Can Juice Jacking Happen on iPhone and Android?
Yes.
Both Android and iOS devices can be affected.
Modern devices include security prompts, but:
• Users ignore them
• Some malware bypasses prompts
• Old OS versions are vulnerable
Always keep your OS updated.
Signs You Might Be a Victim
Watch for:
• Phone behaving strangely
• Battery draining fast
• Unknown apps installed
• Pop-ups appearing
• Overheating
• Data usage spikes
If you suspect infection:
• Disconnect immediately
• Turn off data
• Scan device
• Reset if necessary
How to Prevent Juice Jacking (Complete Protection Guide)
Now the most important part.
1. Avoid Public USB Charging Ports
Best solution:
Do not use public USB ports.
Instead use:
✔ Wall power sockets
✔ Your own charger
Power outlets are safer because they do not transfer data.
2. Use a Power-Only Cable
These cables:
• Disable data pins
• Only allow electricity
They prevent data transfer completely.
3. Use a USB Data Blocker
Also called:
“USB Condom”
It blocks data signals and allows only power.
Small device that sits between cable and port.
Highly recommended for travelers.
4. Carry a Power Bank
Safest method:
Carry your own power bank.
No public dependency.
5. Never Tap “Trust” on Unknown Devices
If a popup appears asking:
“Trust this computer?”
Always select:
❌ Don’t Allow
Unless it is your personal laptop.
6. Keep OS Updated
Updates patch vulnerabilities.
Old Android or iOS versions are riskier.
7. Disable Data Transfer Mode
In USB settings, select:
“Charge Only”
Not “File Transfer”
Juice Jacking vs Charging Malware Cables
There are advanced hacking cables like:
• O.MG cable
These look normal but contain Wi-Fi enabled microchips.
They allow remote hacking even from nearby distance.
Never borrow unknown cables.
Why Students & Cyber Learners Must Understand This
Students today:
• Store assignments
• Store passwords
• Use digital banking
• Attend online classes
Juice jacking can:
• Steal exam data
• Leak personal photos
• Compromise accounts
Cyber awareness is essential.
Institutes teaching cybersecurity should include:
✔ USB security
✔ Physical attack awareness
✔ Device hardening practices
Is Juice Jacking Common in India?
Confirmed large-scale cases are limited.
However:
Security agencies warn that it is technically possible.
Public awareness campaigns have increased globally.
Prevention is better than panic.
Final Verdict
Juice jacking is real.
It exploits human behavior and convenience.
While large-scale cases are rare, the technical possibility exists.
Best practice:
Avoid public USB charging.
Use power outlets or your own power bank.
Cybersecurity is not just online — it includes physical access points too.
Stay alert. Stay informed.




